In this tutorial we will see how to deploy FastAPI on Azure App Service Linux Plan. The FastAPI will have PostgreSQL database and Asynchronous REST Endpoints. We will create a PostgreSQL database on Azure and App Service Plan to host FastAPI on Azure ☁️.
In case you are interested in development of the FastAPI app that is being deployed in this tutorial, it is recommended to go through the article that will walk you through Implementing Async REST APIs in FastAPI with PostgreSQL CRUD.

Table of Contents
- Prerequisites
- Architectural Overview of Deploying FastAPI on Azure App Service
- Create & Configure Azure Database for PostgreSQL server
- Create & Configure Azure App Service (Linux)
- Configure to Deploy FastAPI on Azure App Service from GitHub
- Video Tutorial
Prerequisites
- Internet Connectivity
- Github account
- Fork this repository to your GitHub account
- Azure Account
- Azure App Service (Linux, F1: Free or B1: Basic)
- Azure Database for PostgreSQL servers (Basic, 1 vCore(s), 50 GB)
We will accomplish the deployment of FastAPI on Azure ☁️ that has asynchronous REST Endpoints and PostgreSQL database as a persistence in three steps
- Create & Configure Azure Database for PostgreSQL server
- Create & Configure Azure App Service (Linux)
- Configure to Deploy FastAPI on Azure App Service from GitHub
Architectural Overview of Deploying FastAPI on Azure App Service
The following image shows the Architecture of how the FastAPI is deployed on Azure App Service.
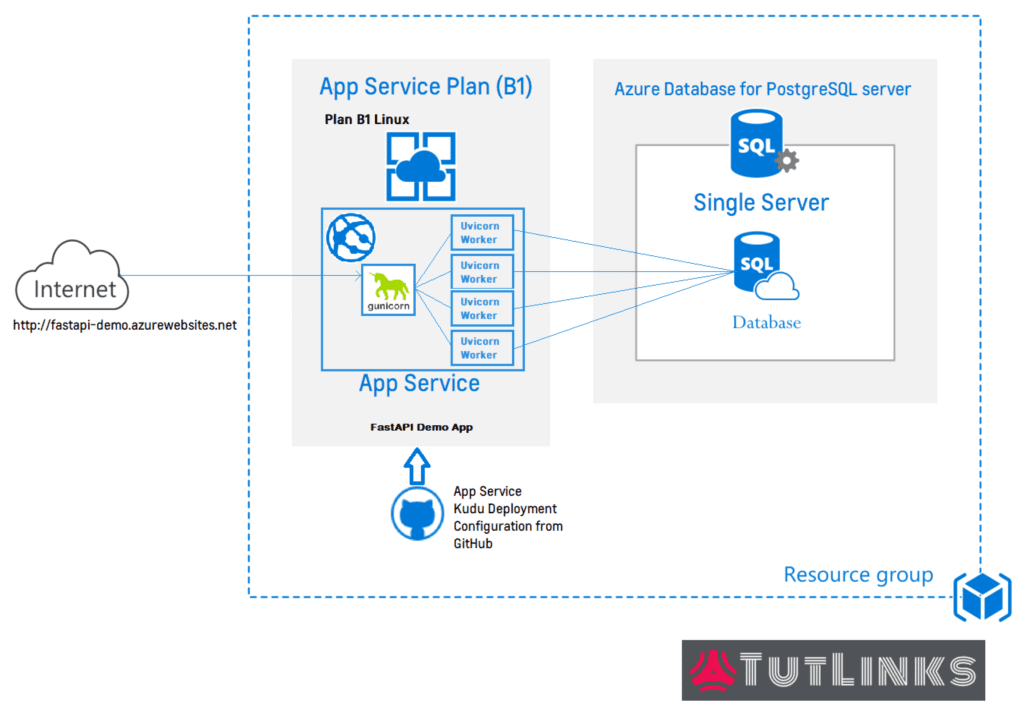
Once we have deployed, our FastAPI running on Azure App Service can be visualized as mentioned in the architectural diagram.
The web request can be made to Azure App Service which can be accessed via an URL of the form {your-app-service-name}.azurewebsites.net unless you configure Custom Domain to the App Service.
The request is received by Gunicorn which spwans the FastAPI running on four child worker processes with the help of Asynchronous Uvicorn Worker Class. Each of the Uvicorn worker class runs FastAPI app on a randomly chosen process id (pid) and the request delegation is handled by the Gunicorn that runs on a process id that can be configured to run on specified port.
The web request is delegated to one of the instance of the FastAPI application that is available among these worker processes. All the four instances in this setup will talk to the same database created in the Azure Database for PostgreSQL Server. The database context for each of the worker processes is isolated from the other, because we are establishing the connection to the database in the @app.on_event("startup") event of the FastAPI. Similarly we are disconnecting from the database in @app.on_event("shutdown") event of the FastAPI. The startup and shutdown events are invoked for each of the worker processes. Thus any requests that involve interaction with the database are handled within the process.
The App service deployment configuration will detect any changes to the GitHub repository it is configured with. The deployment configuration with Kudu pulls and deploys the code to the App Service automatically.
Full Source Code of this tutorial is available on fastapi-postgresql-azure-deploybranch of this repository.
Create & Configure Azure Database for PostgreSQL server
Create PostgreSQL server on Azure
Follow these steps to create Azure Database for PostgreSQL server.
- Login to portal.azure.com
- Type PostgreSQL in the search box located at the top center of Azure Portal and choose
Azure Database for PostgreSQL serversin theServicessection of search results. - Click on
Addbutton to a new PostgreSQL server - Select Azure Database for PostgreSQL deployment option depending on your need. I’ll be choosing
Single Serverand clickCreate. - Under the
Basicstab ofSingle Serverfor PostgreSQL configuration wizard provide Project Details, Server Details
Provide Project Details
- Choose Subscription of your choice in case you have multiple options or proceed with default chosen option.
- For Resource Group, click on Create new and give a meaningful name such as
FastAPI-PostgreSQL-rg
A Resource group provides logical grouping of all the resources you want to maintain for your project. Any new services or features that you want to add that belongs to this project (such as PostgreSQL database or Storage Accounts) can be created and associated to this Resource Group.
Provide Server Details
Enter required settings for this server, including picking a location and configuring the compute and storage resources.
- Provide
Server nameasfastapi-pgsql-srvor any other name of your choice - Leave the
Data sourceoption as is set toNone - Choose
Locationof your choice or go on with the default chosen option - Choose PostgreSQL server
Versionof 10 or above - For
Compute + storageclick onConfigure serverthat will land you or server Configure blade - Click on
Basictab among three available tabsBasic,General PurposeandMemory Optimized - Slide
vCoreto have cores based on your need. I moved the slider to choose 1 vCore - Slide
Storageto increase or decrease theBasic storagecapacity for your PostgreSQL database server - Leave all other options as is and click on
OK
Create Administrator account for Azure database for PostgreSQL
Provide credentials that will allow you to connect to the PostgreSQL database server.
- Provide
Admin usernameof your choice - Provide
Passwordand ensure theConfirm passwordto match password provided - Click on
Review + createand then clickCreate - The database server creation will typically take 5-7 minutes and hold back till the resource creation completes
- Click on
Go to Resourceor manually navigate to the PostgreSQL server created
Configure Azure database for PostgreSQL server
Navigate to the PostgreSQL server created and you will be landed on Overview page. Under Settings click on Connection security
Allow access to Azure services
If you want this database server to be access by all Azure Services across Azure Portal including the resources that are not in active subscription where this server lies, toggle the Allow access to Azure services to Yes. I’ll leave it as No which is default as my web app will be within the same subscription that of the database server.
Access Azure PostgreSQL database server from pgAdmin on local PC
In order for you to access the database server on your PC via pgAdmin, then click on Add client IP located at the top of the Connection security page. This will add a Firewall rule name with the IP address of your PC / Laptop from where you want to access this database server via pgAdmin.
- Leave the Enforce SSL settings to
ENABLEDunless you want to turn it off for obvious reasons - Finally, click on
Savebutton located at the top of theConnection securitypage
Connect to Azure PostgreSQL Database server from pgAdmin
If you do not have PostgreSQL on your PC you may want to install it by following the instructions mentioned in this article Install PostgreSQL Without Admin Rights on Windows 10 OS
Open Create-Server Wizard
Under the Servers tree node to the extreme left, right click on the node, choose create and click on Server… to create a new server. You can also click Add New Server under Quick Links that appears in the center of the page.
Specify a Server Name
Under General tab of the Create – Server wizard, specify the name of the server you want to create. This could be any noticeable name of your choice or something that might indicate the logical name of the data that the database server holds.
Specify Connection Details
To provide values for Connection details, open the Overview page of the PostgreSQL database server on Azure.
- Provide
Host name/addresswith value ofServer namefield. - Provide
Portwith value of5432 - Provide
Usernamewith value ofAdmin username - Provide
Passwordwith value given when creating Administrator account with username and password. - If you forgot the password, in Overview pane of Azure PostgreSQL server find and click
Reset passwordand then providePasswordandConfirm passwordand save it and provide the same in password textbox of pgAdmin Connection detail.
SSL Configuration
Azure database for PostgreSQL server has default configuration to Enforce SSL connection. So in order for you to be able to connect to it from pgAdmin perform the following while creating server on pgAdmin to connect to it.
- Click on the SSL tab of the
Create - Serverpopup of pgAdmin - Change the value of
SSL modedropdown fromPrefertoRequire - Finally Click on Save and you should be able to see the Azure PostgreSQL server visible in the pgAdmin Servers list
- The new server will appear in the left pane under the Servers tree as a child node
Create a database in PostgreSQL via pgAdmin4
- Under the databases you will find the default
postgresdatabase - Locate and right click on the database node of the Azure database for PostgreSQL server in pgAdmin. Choose create and then click on
Database… - In the General tab of the Create – Database wizard, give a name of your choice to be set for the new database being created. Feel free to modify the encoding in the Definition tab of the wizard. By default it will be set to UTF-8. I will be giving the database name as
fastapi - Click on Save to create the database and you should see the new database under the server we have created
Create & Configure Azure App Service (Linux)
Create Azure App Service
Follow the steps to create Azure app service for Linux.
- Login to portal.azure.com
- Locate App Services and Click on Add
Provide Project Details
- On Create Web App wizard under Basics tab choose Subscription in case you have multiple options
- For Resource Group, click on Create new and give a meaningful name such as
FastAPI-PostgreSQL-rg
A Resource group provides logical grouping of all the resources you want to maintain for your project. Any new services or features that you want to add that belongs to this project (such as PostgreSQL database or Storage Accounts) can be created and associated to this Resource Group.
Provide Instance Details
- Provide meaningful name for your FastAPI deployment on Azure App service. It should be unique across all the web app names available in the Azure. I’ll go on with
fastapi-pgsql-demoand once the FastAPI is deployed on Azure app service, I will be able to access it via the urlfastapi-pgsql-demo.azurewebsites.net. You can provide the App Service name of your choice - For
Publish modechooseCode. Surprise, no docker is being used here! - Choose
Runtime stackto be Python 3.6 or higher. I will be choosing Python 3.8 - Choose Linux as
Operating System - Leave the
Regionas default chosen option unless you want to select a different region of your choice
Choose App Service Plan
- For
Linux Plan (Region)click on Create new and Provide a meaningful name for your App Service Plan. I’ll be naming itfastapi-pgsql-asp - For
Sku and sizeclick onChange sizelink and you will land onSpec Pickerblade. For production workloads you can choose among any of the Standard (S1 / S2 / S3) or Premium (P1V2 / P2V2 / P3V2) pricing tiers. But for the sake of tutorial and save some money 😉 I will go on with the B1. You can also choose the Basic (B1) core for Linux which is free for the first 30 days from the date of creation of App Service Plan. Also, B1 and above plans facilitate to point custom domains or configure custom SSL to all the web apps hosted under this App Service Plan. Free F1 plan does not have these features. - Under
Dev / Test (For less demanding workloads)tab ofSpec Pickerchoose B1 located under Recommended pricing tiers and click onApply. If you are following this tutorial for practice purposes, do not forget to delete all the resources under the resource group after the tutorial is over. - Click on
Review + Createand verify all the details and click onCreate. The Web App creation will take 3-5 minutes.Once done click onGo to Resource.
Configure Azure App Service
Open the App Service that you have created by manually navigating to it.
- Under
Settings->Configurationopen tabGeneral Settingsof App Service - Give the
Startup Commandwith the command to start FastAPI on Azure App Service
gunicorn -w 4 -k uvicorn.workers.UvicornWorker main:app
- Navigate to
Settings->Configurationopen tabApplication Settingsof App Service - Add new application settings with names
db_username,db_password,host_server,database_name,ssl_modeanddb_server_portand corresponding values for each of the settings with that of Azure database for PostgreSQL server created.
Configure to Deploy FastAPI on Azure App Service from GitHub
Perform the following steps to configure a Continuous Deployment of our FastAPI app hosted on GitHub on to Azure App Service. This will ensure that whenever a new commit is pushed to the configured branch, the new changes will be deployed to the Azure App Service.
Disclaimer: It is recommended to have tests and other sanity to be added as a part of the Continuous Delivery pipeline. Ensure to have all tests pass before deploying to avoid any unforeseen surprises.
- Navigate to
Deploymentsection of our Azure App Service for Linux that we have created and click onDeployment Center - On
Continuous Deployment (CI / CD)step, chooseGitHuband if prompted, authorize your GitHub account by providing credentials and click onContinueto proceed. - Choose
Build ProviderasApp Service build serviceand click onContinue. - In
Configurestep, we will tell where to pullCodefrom with details as below.Organization– If you have multiple organizations, choose the organization where your FastAPI repo is located. Otherwise go on with default Organization chosen.Repository– Locate and choose the repository based on the name.Branch– Choose the branch to deploy to the Azure App Service every time a change is pushed to.- Click on
Continueto proceed.
- In
Summarystep, verify Source Control properties and build provider and clickFinish. - Wait for the first initial build to pull the code from configured GitHub repository until you see status
Success (Active).Azure App Service Deployment runs the oryx build, an intelligent rule based application builder that has some predefined configurations to detect the code base to be built and performs suitable actions. For example if you are trying to deploy a Python based application, it will automagically install virtual environment and looks for the presence ofrequirements.txtif any and installs the dependencies. It also try to spin up the application by looking formain.pyorapp.pyusing python interpreter.
After the successful deployment of FastAPI on Azure App service, navigate to your-app-service-name.azurewebsites.net/docs to access the OpenAPI (formerly known as Swagger) spec.
Video Tutorial
Congratulations 🎉, you have successfully learnt how to deploy FastAPI on Azure App Service. Bookmark 🔖 (Ctrl + D) this page for a quick reference.
Check these resources to deploy FastAPI on On Premises and other Cloud Platforms



Pingback: Implementing Async REST APIs in FastAPI with PostgreSQL CRUD – TutLinks
Pingback: Deploy FastAPI on Ubuntu and Serve using Caddy 2 Web Server – TutLinks
Pingback: Deploy FastAPI app on Google Cloud Platform – TutLinks